281-772-9069 info@brilliancenutrition.com
D-Chiro-Inositol: A Natural Supplement for Improving Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disorder characterized by coexisting reproductive dysfunction and metabolic abnormalities. It is the most common endocrine disorder among women of childbearing age, with a prevalence of 6% to 10% in this population. The condition is defined by an abnormally high number of follicles (more than 12) or the presence of cysts in the ovaries.
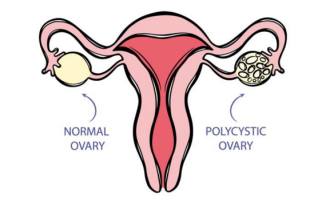
Persistent anovulation, immature follicles, hyperandrogenism, and insulin resistance are its core features. Beyond irregular menstruation and infertility, PCOS presents a range of symptoms including amenorrhea, anovulation, hirsutism, obesity, and polycystic ovarian morphology. The majority of menstrual irregularities are caused by PCOS, which has become one of the leading causes of female infertility.
I. D-Chiro-Inositol: A "Nemesis" of PCOS for Blood Glucose Regulation and Metabolic Syndrome Improvement
D-chiro-inositol (DCI) is a bioactive substance used to alleviate PCOS symptoms. Physicians often recommend PCOS patients supplement with DCI alongside self-management to improve symptoms, restore regular menstrual cycles, and reestablish ovulation.
What is D-Chiro-Inositol?
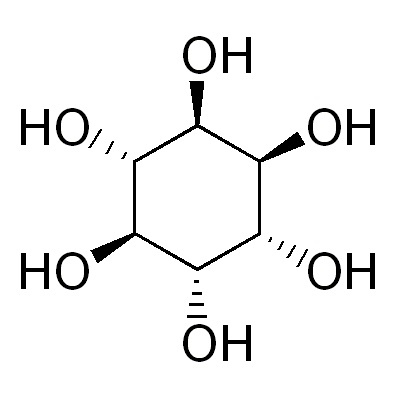
D-chiro-inositol (DCI) is one of the nine optically active isomers of inositol. Classified under the B-vitamin family, it is also known as vitamin B8. Highly soluble in water, DCI exists in nature either in free form or as galactosyl derivatives in plants such as carob, buckwheat, and soybeans.Carob, a legume native to the Mediterranean coast, has the highest natural DCI content among plants.
As early as 1999, Dr. Larner discovered that DCI could improve insulin resistance, increase ovulation rates in women with PCOS, and enhance lipid profiles. Acting as an insulin sensitizer, DCI is referred to as the "second messenger of insulin."
Insulin resistance is the "common soil" for metabolic diseases: its prevalence reaches 69.7% in diabetes and 50-70% in PCOS. According to international clinical trial data, supplementing with 500-1000mg of DCI daily effectively reduces insulin resistance in patients with PCOS and gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM).
A key advantage of DCI is its excellent tolerability—it does not cause side effects like diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting—while being safe and natural. Notably, it delivers similar therapeutic effects to metformin, a pharmaceutical drug used to improve insulin resistance. This important cyclic sugar alcohol is widely used in medicine and healthcare, gaining attention for its unique bioactivity and health benefits, particularly in regulating blood glucose and improving metabolic syndrome.
II. Multiple Efficacies: Blood Glucose Regulation, Liver Protection, PCOS Improvement, and Antioxidant-Anti-Inflammatory Effects
As a natural human metabolite, DCI is an indispensable precursor for membrane phospholipids and has multiple validated physiological functions.
(1) Involvement in Insulin Signaling
DCI is present in insulin target organs such as adipose tissue, muscle, and the liver, highlighting its close association with insulin function.
Mechanism of Action
In the insulin pathway, DCI is recognized as a key molecule in the signaling cascade, acting as both an insulin mediator and sensitizer. It is converted into DCI-IPG, which participates in insulin receptor signal transduction. By activating glycogen synthase (GS) and pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH), DCI promotes glycogen synthesis and lowers blood glucose.Specifically, insulin stimulates the phospholipase-mediated release of DCI-IPG, a process closely linked to insulin sensitivity.
DCI is naturally present in the blood and urine of healthy individuals. However, in patients with type 2 diabetes, DCI is barely detectable in the blood, while urinary DCI levels are several times higher than normal. Metabolic disorders in type 2 diabetes lead to excessive DCI loss, impairing or weakening insulin signal transmission.
When DCI levels are low, insulin signal transduction is disrupted, increasing cellular insulin resistance (IR) and elevating blood insulin concentrations, resulting in hyperinsulinemia. Hyperinsulinemia reduces the synthesis of sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) in the liver, raising free androgen levels in the blood and causing hyperandrogenism, which in turn triggers a range of symptoms.
1. Blood Glucose-Lowering Effect
DCI exerts hypoglycemic effects by promoting the expression of GLUT4, IR, and IRS-2 proteins in liver cells, thereby reducing insulin resistance and lowering blood glucose.
Impact of DCI on dynamic changes in random blood glucose in db/db mice:
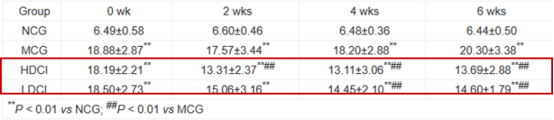
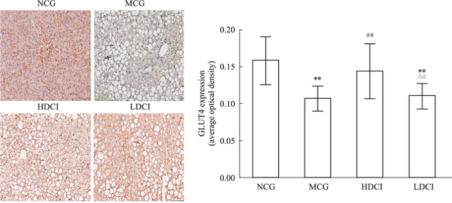
▲Immunohistochemistry of GLUT4 protein expression in liver tissue of db/db mice
2. Liver Protection Effect
DCI protects the liver by reducing liver damage and alleviating steatosis and fibrosis in liver tissue.
Morphological structure of liver tissue in db/db mice:
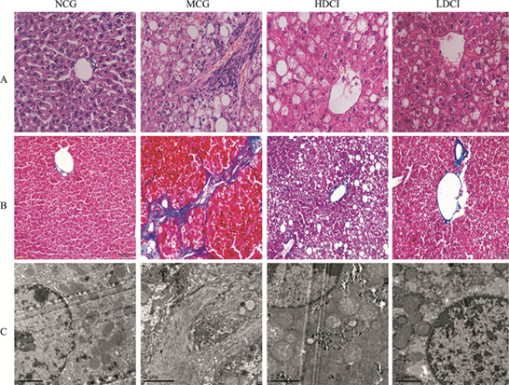
▲DCI inhibits hepatic lipid accumulation and adipocyte hypertrophy in HFD-fed mice
DCI increases adiponectin levels to reduce obesity and hepatic lipid deposition caused by a high-fat diet. It may alleviate hepatic lipid accumulation and hyperlipidemia by promoting adiponectin synthesis in white adipose tissue and activating the AdipoR-AMPKα/PPARs pathway in the liver.
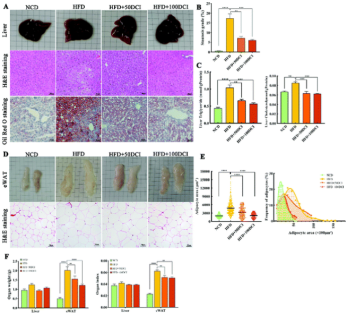
▲ DCI inhibits hepatic lipid deposition and adipocyte hypertrophy in mice fed with high-fat diet
(2) Involvement in the Gonadotropin Pathway
The World Health Organization estimates that PCOS affects 8-13% of women of childbearing age, arising from interacting concurrent endocrine changes. Among PCOS patients, 74% experience anovulatory cycles. PCOS is the most common cause of ovulation cessation and infertility, with a tendency toward familial aggregation.
Women with PCOS may have elevated levels of the following hormones:
Sex hormone secretion in the human body is regulated by signaling between the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries—an interactive, interdependent, and mutually restrictive system known as the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Ovarian (HPO) axis.
Since these three organs are anatomically distant, regulatory signals are transmitted via hormones. Hormonal imbalance disrupts HPO axis regulation, leading to adverse symptoms.
PCOS women with insulin resistance are most prone to DCI deficiency. Insufficient DCI impairs glucose metabolism, maintaining high insulin levels that stimulate the ovaries to produce excess testosterone. Women normally have approximately 10% of the testosterone levels of men; sustained increases in testosterone disrupt hormonal balance and trigger multiple symptoms.
DCI regulates hormone levels by modulating SHBG. It supports insulin signal transmission, enabling cells to absorb glucose even at low insulin concentrations, thereby alleviating hyperinsulinemia. In other words, DCI supplementation improves insulin sensitivity, lowers blood insulin levels, restores normal hepatic SHBG synthesis, and reduces free androgens in the blood—ultimately regulating menstrual cycles and restoring ovulation.
DCI also acts as an LH sensitizer, reducing endogenous LH synthesis and improving LH signaling—likely due to the involvement of inositol and inositol phosphates in the LH signaling pathway. Additionally, DCI inhibits aromatase expression: aromatase is the only enzyme responsible for estrogen synthesis, catalyzing the aromatization of the androgen A-ring to produce estrogen. DCI effectively suppresses androgen catabolism. Both estrogen and gonadotropins signal via phosphoinositides.
1. PCOS Improvement
Plasma DCI concentrations in PCOS women with insulin resistance are less than half those of healthy women, while their urinary DCI clearance rate is 6 times higher. Elevated DCI clearance shows a strong correlation with severe insulin resistance.
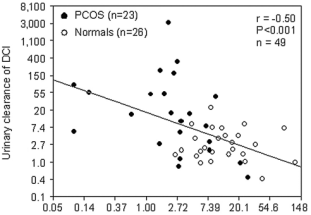
▲Correlation between urinary DCI clearance and insulin sensitivity (Si) in PCOS patients vs. healthy women
2. Health Improvement in PCOS Women

DCI alleviates menstrual irregularities and acne in women by regulating hormonal balance and menstrual cycles. Supplementation is necessary when endogenous DCI levels are insufficient.
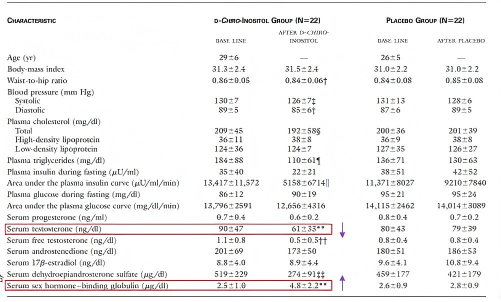
Characteristics of 44 PCOS women at baseline and after 6-8 weeks of DCI or placebo administration.
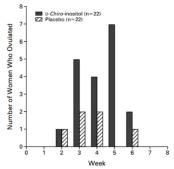
▲Number of ovulating PCOS women during 6-8 weeks of DCI or placebo administration
DCI improves insulin resistance in women with PCOS and irregular menstrual cycles.
Impact of DCI (1000mg-1500mg/day) on PCOS women over different treatment durations:
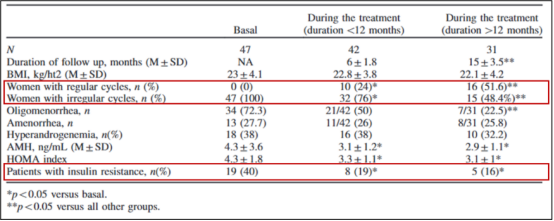
① The proportion of women with oligomenorrhea or amenorrhea decreases as menstrual regularity increases;
② The proportion of subjects with insulin resistance declines.
Elevated LH is a hallmark of PCOS and may inhibit ovarian follicle maturation. Furthermore, metabolic traits are closely linked to gonadal function. DCI improves ovarian function and metabolism, with superior efficacy in reducing hyperandrogenism.
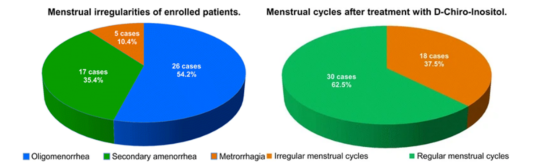
▲Menstrual irregularities in patients; Menstrual cycles after DCI treatment
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) affects 2%-14% of pregnant women worldwide, defined as glucose intolerance first detected during pregnancy. Unlike overt diabetes, GDM significantly increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Prolactin, a pregnancy-related factor, may regulate metabolism and affect insulin secretion, leading to maternal hyperglycemia. Dietary DCI supplementation during pregnancy serves as an effective strategy for GDM management, benefiting both maternal and fetal health.
Comparison of blood glucose indicators and homeostasis model assessments before and after treatment across groups:
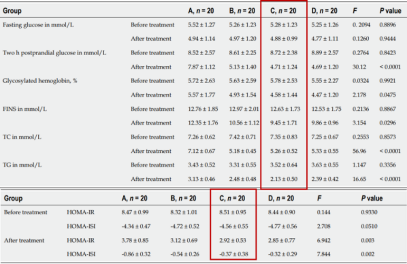
Group A: Placebo + 400μg folic acid/day;
Group B: 1500mg MI twice daily;
Group C: 250mg DCI twice daily;
Group D: 1500mg MI + 250mg
*DCI twice dailyDCI simultaneously improves glucose and lipid metabolism in the HOMA homeostasis model, significantly reducing HOMA-IR and increasing HOMA-ISI.
(3) Antioxidative Stress
Mechanism of Action
DCI resists oxidative stress by regulating the reduced glutathione/oxidized glutathione (GSH/GSSG) ratio to mitigate oxidative damage. It downregulates TNF-α and IL-6, key modulators of inflammatory responses, helping to reduce proinflammatory states.
1. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects
DCI regulates cellular redox status and exerts anti-inflammatory effects.
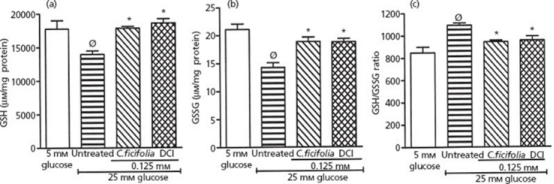
▲Effect of 48-hour DCI treatment on redox status in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
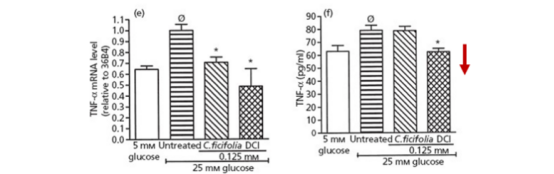
▲Effect of 48-hour DCI treatment on TNF-α mRNA expression and protein levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
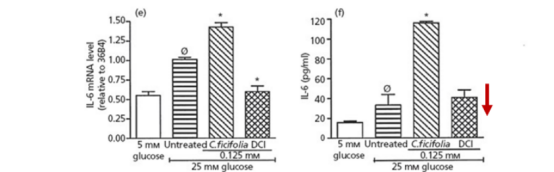
▲Effect of 48-hour DCI treatment on IL-6 mRNA expression and protein levels in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
III. High Safety and Multi-National Certification: Food, Dietary Supplement, and Natural Food Flavor
In today’s global food market, DCI is a novel functional ingredient gaining widespread attention for its safe, unique benefits for women’s health and nutritional value. It is primarily used in nutraceuticals, functional foods, and dietary supplements to maintain physiological balance in women with PCOS.
DCI is generally recognized as safe and effective, with no toxicity or adverse effects. Short-term use at moderate doses, or even periodic use, is recommended; specific dosages should follow medical advice.
Non-toxic and High SafetyAcute oral toxicity tests and reverse mutation assays (conducted in South Korea and Japan) confirm the non-toxicity of DCI raw materials. Oral DCI has high safety, even for pregnant women.
No Side EffectsAs an endogenous nutrient, DCI is natural and free of side effects.In a 1999 study by J. E. Nestler et al., 44 obese PCOS women took 1200mg of DCI orally once daily for 6-8 weeks with no adverse reactions.
IV. 100-Ton Scale Market: Broad Development Prospects as a Food Ingredient
Currently, the global market scale of DCI raw materials is around 100 tons (overseas), primarily used for PCOS management. The raw material is priced at approximately RMB 1,000/kg, resulting in a raw material market scale of RMB 100 million (typical of plant extract markets).

Globally, 10% of women and 30% of adolescent girls suffer from menstrual irregularities; in China, over 40 million women are affected.10% of Chinese women of childbearing age (4 million people) experience infertility due to metabolic syndrome or PCOS.
Applications of DCI-Related Products
Conclusion:
The human kidneys synthesize at least 2000mg of myo-inositol daily from glucose, part of which is converted to DCI by epimerase. While this conversion occurs normally in healthy individuals, PCOS patients lack this enzyme, leading to extremely low conversion rates—necessitating additional DCI supplementation.
Currently, DCI products on the market are mainly derived from carob extracts, available in forms such as powder and tablets. Synthetic biology, with its advanced technologies, provides high-purity, safe, and effective DCI, unlocking new growth opportunities in the DCI market.